In this C++ tutorial, you will learn about two interesting types of pointers; void pointers and Null Pointer. These pointers will be discussed in conjunction with syntax, usage and example.
Pointer to Void
General Syntax:
void* pointer_variable;
Void is used as a keyword.
Referring back to pointer definitions and usage, it is known that the data type the pointer variable defines is the same as the data type the pointer points to. The address placed in a pointer must have the same type as the pointer.
For example:
int i;
float f;
int* exf;
float* test;
then
exf=&i;
Is correct because the address of integer variable is stored in an integer pointer.
If a user writes the statement:
exf=&f;
Then this statement produces an error. The address of the float variable is stored in an integer pointer that is incorrect.
Similarly, if the programmer tries to place the address of an integer variable to a float pointer, such as:
test=&i;
The above statement will also show an error.
The Pointer to Void is a special type of pointer that the programmer can use to point to any data type.
Using the above example, the programmer declares pointer to void in this manner:
void* sample;
Using the above example’s definition and assigning the pointer to void to the address of an integer variable is perfectly correct.
sample=&i;
Using the above example to define the pointer to void and assign the pointer to void to the address of a float variable as below is also perfectly correct.
sample=&f;
Pointer to void, or a void pointer, is a special type of pointer that has a great facility of pointing to any data type. There are limitations in the usage of void pointers that are explained below.
The concept of dereferencing using the operator * has been explained in an earlier section of this tutorial. The programmer must note that void pointers cannot be de-referenced in the same manner. Direct dereferencing of void pointer is not permitted. The programmer must change the pointer to void as any other pointer type that points to valid data types such as, int, char, float and then dereference it. This conversion of pointer to some other valid data type is achieved by using the concept of type-casting (refer to type-casting section of this tutorial).
NULL Pointer:
The concept of NULL pointer is different from the above concept of void pointer. NULL pointer is a type of pointer of any data type and generally takes a value as zero. This is, however, not mandatory. This denotes that NULL pointer does not point to any valid memory address.
For example:
int* exforsys;
exforsys=0;
The above statement denotes exforsys as an integer pointer type that does not point to a valid memory address. This shows that exforsys has a NULL pointer value.
The difference between void pointers and NULL pointers:
A Void pointer is a special type of pointer of void and denotes that it can point to any data type. NULL pointers can take any pointer type, but do not point to any valid reference or memory address. It is important to note that a NULL pointer is different from a pointer that is not initialized.
For example, if a programmer uses the program below:
#include <iostream>using namespace std;
int *exforsys=NULL;
void main()
{*exforsys=100;
}
The output of the above program is NULL POINTER ASSIGNMENT, which will result in:
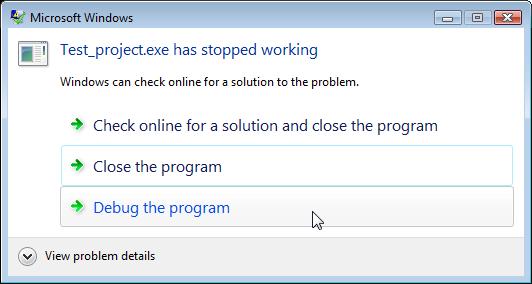
The above program will result in a runtime error. This means that the pointer variable exforsys is not assigned any valid address and, therefore, attempting to access the address 0 gives the above error message.
[catlist id=165].
