Database Triggers
A database triggers is stored PL/SQL program unit associated with a specific database table or view. The code in the trigger defines the action the database needs to perform whenever some database manipulation (INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE) takes place.
Unlike the stored procedure and functions, which have to be called explicitly, the database triggers are fires (executed) or called implicitly whenever the table is affected by any of the above said DML operations.
Till oracle 7.0 only 12 triggers could be associated with a given table, but in higher versions of Oracle there is no such limitation. A database trigger fires with the privileges of owner not that of user
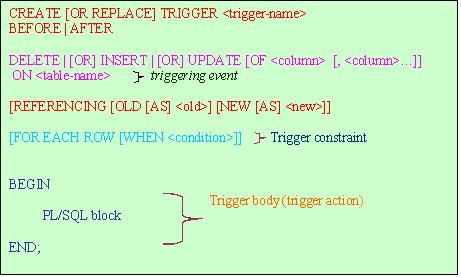
A database trigger has three parts
- A triggering event
- A trigger constraint (Optional)
- Trigger action
A triggering event can be an insert, update, or delete statement or a instance shutdown or startup etc. The trigger fires automatically when any of these events occur A trigger constraint specifies a Boolean expression that must be true for the trigger to fire. This condition is specified using the WHEN clause. The trigger action is a procedure that contains the code to be executed when the trigger fires.
Types of Triggers
The following are the different types of triggers.
Row triggers and statement triggers
A Row trigger fires once for each row affected. It uses FOR EACH ROW clause. They are useful if trigger action depends on number of rows affected.
Statement Trigger fires once, irrespective of number of rows affected in the table. Statement triggers are useful when triggers action does not depend on
Before and afterTriggers
While defining the trigger we can specify whether to perform the trigger action (i.e. execute trigger body) before or after the triggering statement. BEFORE and AFTER triggers fired by DML statements can only be defined on tables.
BEFORE triggers The trigger action here is run before the trigger statement.
AFTER triggers The trigger action here is run after the trigger statement.
INSTEAD of Triggers provide a way of modifying views that can not be modified directly using DML statements.
LOGON triggers fires after successful logon by the user and LOGOFF trigger fires at the start of user logoff.
Points to ponder
- A trigger cannot include COMMIT, SAVEPOINT and ROLLBACK.
- We can use only one trigger of a particular type .
- A table can have any number of triggers.
- We use correlation names :new and :old can be used to refer to data in command line and data in table respectively.
Triggers on DDL statements
DDL trigger are of the following types
BEFORE CREATE OR AFTER CREATE trigger is fired when a schema object is created.
BEFORE OR AFTER ALTER trigger is fired when a schema object is altered.
BEFORE OR AFTER DROP trigger is fired when a schema object is dropped.
A trigger can be enabled means can be made to run or it can disabled means it cannot run. A trigger is automatically enabled when it is created. We need re-enable trigger for using it if it is disabled. To enable or disable a trigger using ALTER TRIGGER command, you must be owner of the trigger or should have ALTER ANY TRIGGER privilege. To create a trigger you must have CREATE TRIGGER privilege, which is given to as part of RESOURCE privilege at the time of user creation.
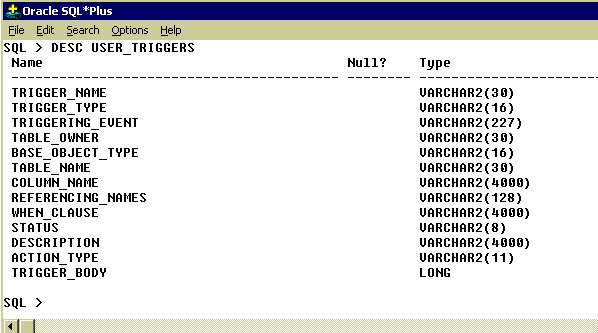
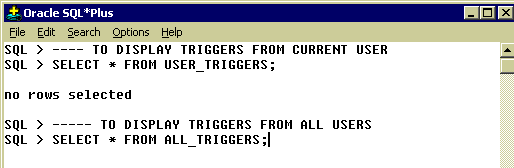
Following figures give more understanding about triggers

{mospagebreak}
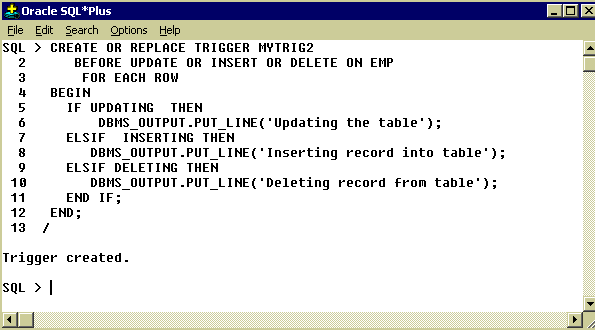
Handling multiple situations
A trigger can be used to handle multiple situations as shown in the following example. By using conditional predicates UPDATING, INSERTING, or DELETING we can handle each situation.
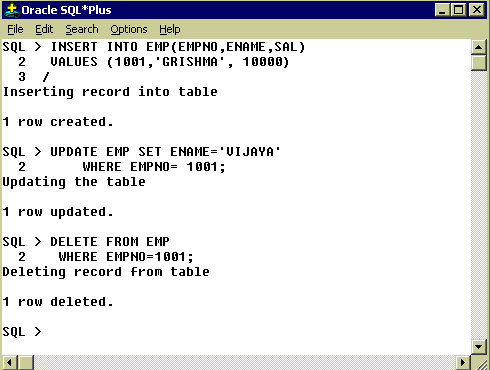
CORRELATION NAMES
While using row triggers, the trigger action statement can access column values of the row that is being processed currently. This is done using correlation names. There exist two correlation names for every column of the table, one for the column old value and the other for its new value. We use qualifier NEW with column name for new values and qualifier OLD is used to refer old value of the column.
Example:
IF :new.sal < :old.sal THEN
……
The REFERENCING option is used to avoid name conflicts between correlation names and table names. For example if you are using a table by name new or old with field names say SNO, NAME (though it is a very rare situation) then the ambiguity arises. To avoid this we use REFERENCING option.
Mutating Table: is a table that is presently under modification by INSERT, UPDATE, or DELETE statement, or a table that has referential integrity constraint with DELETE CASCADE OPTION.
Constraining Table: is a table, which is to be read by triggering statement either directly or indirectly.
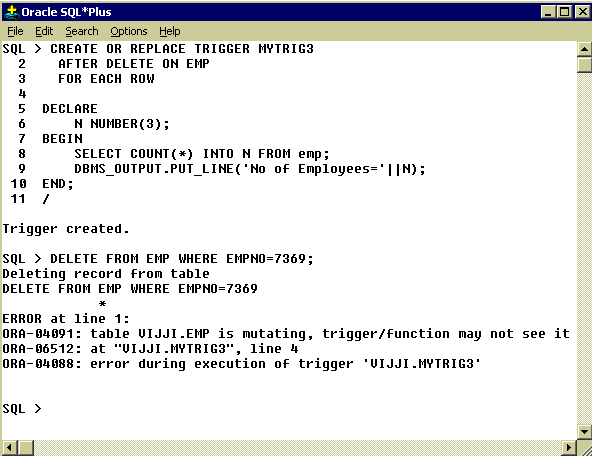
In the above example when we tried to delete a row using SQL statement (Mutating Table) , which fires AFTER DELETE trigger. The body of this trigger is having a select statement that tries to read the table. This operation is not allowed by oracle. Hence we received a runtime error and total action is rolled back by Oracle. (The row is not deleted)
[catlist id=172].
