Array is a collection of same type elements under the same variable
identifier referenced by index number. Arrays are widely used within programming
for different purposes such as sorting, searching and etc. Arrays allow you to
store a group of data of a single type. Arrays are efficient and useful
for performing operations . You can use them to store a set of high scores in a
video game, a 2 dimensional map layout, or store the coordinates of a
multi-dimensional matrix for linear algebra calculations.
Arrays are of two types single dimension array and multi-dimension array.
Each of these array type can be of either static array or dynamic array. Static
arrays have their sizes declared from the start and the size cannot be changed
after declaration. Dynamic arrays that allow you to dynamically change their
size at runtime, but they require more advanced techniques such as pointers and
memory allocation.
It helps to visualize an array as a spreadsheet. A single dimension array is
represented be a single column, whereas a multiple dimensional array would span
out n columns by n rows. In this tutorial, you will learn how to declare,
initialize and access single and multi dimensional arrays.
Single Dimension Arrays
Declaring Single Dimension Arrays
Arrays can be declared using any of the data types available in C. Array size
must be declared using constant value before initialization. A single
dimensional array will be useful for simple grouping of data that is relatively
small in size. You can declare a single dimensional array as follows:
<data type> array_name[size_of_array];
Say we want to store a group of 3 possible data information that correspond
to a char value, we can declare it like this:
Note: In C language the end of string is marked by the null
character ‘�’. Hence to store a group of 3 possible string data. We declare the
array as char game_map[4]; This applies for char type array.
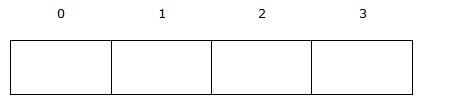
One-dimensional string array containing 3 elements.
| Array Element |
game_map[0] |
game_map[1] |
game_map[2] |
game_map[3] |
| Data |
S |
R |
D |
� |
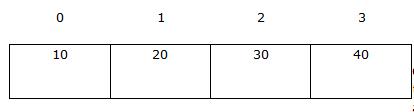
One-dimensional integer array containing 3 elements.
| Array Element |
emp_code[0] |
emp_code[1] |
emp_code[2] |
| Data |
7 |
5 |
8 |
Initializing Single Dimension Arrays
Array can be initialized in two ways, initializing on declaration or
initialized by assignment.
Initializing on Declaration
If you know the values you want in the array at declaration time, you can
initialize an array as follows:
Syntax:
<data type> array_name[size_of_array] = {element 1, element 2, ...};
Example:
char game_map[3] = {'S', 'R', 'D'};
This line of code creates an array of 3 chars containing the values ‘S’, ‘R
‘, and ‘D’.
Initialized by Assignment
char game_map[3];
game_map[0] = 'S';
game_map[1] = 'R';
game_map[2] = 'D';
Accessing Single Dimension Array Elements
Arrays are 0-indexed, so the first array element is at index = 0, and the
highest is size_of_array – 1. To access an array element at a given index you
would use the following syntax:
array_name[index_of_element];
To set an element of an array equal to a value you would write:
array_name[index_of_element] = value;
To access one of the game_map element:
game_map[0]; //value of 'S'
game_map[1]; //value of ' R'
game_map[2]; //value of 'D'
Trying to access a value outside the bounds of index 1 through size_of_array
– 1, results in runtime errors. Your compiler will not complain, but your
program will crash when it executes.
For example:
will lead to a runtime error and you program would crash because you tried to
access a memory location outside the bound of the array, otherwise known as a
segmentation fault.
{mospagebreak title=C Multidimensional Arrays}
Multidimensional Arrays
Arrays can have more than one dimension. Two dimensional arrays are widely
used for tables, neural networks and etc. You can have as many dimensions as you
would like but you have to consider the complexity of the code as you add new
dimension. Multidimensional arrays allow you to store data in a spreadsheet or
matrix like format.
Declaring Multidimensional Arrays
To declare a multidimensional array:
<data type> array_name[size_of_first_dimension][size_of_second_dimension] ...
A very good example is the creation of 2D maps for games.
This would declare a 2 dimensional array of chars that is 10 columns by 10
rows in size.
You could even do a 3D map for a game using a 3 dimensional array.
char game_map[10][10][5];
You can consider above array as being 10 tiles by 10 tiles on the horizontal
plane, and 5 tiles high on the vertical plane.
Initializing Multidimensional Arrays
Just like single dimension array, you can initialize the multidimensional
array also upon declaration as well as initialize by assignment.
<data type> array_name[size_of_dimension1][size_of_second_dimension2] ... = {{element 1, element 2, element 3, …},.
.
. }
};
array [Y][X]
game_map[2][4]; |
X direction ► |
| Y direction▼ |
game_map[0][0] |
game_map[0][1] |
game_map[0][2] |
game_map[0][3] |
| game_map[1][0] |
game_map[2][1] |
game_map[3][2] |
game_map[4][3] |
char game_map[2][4] = { {'x', 'b', 'f', '�'} , {'b', 't', '�' } };
array [Y][X]
game_map[2][4]; |
X direction ► |
| Y direction▼ |
x |
b |
f |
� |
| b |
t |
� |
empty |
int game_map[2][4];
game_map[0][0]=1; game_map[0][1]=2; game_map[0][2]=3; game_map[0][3]=4
game_map[1][0]=6; game_map[1][1]=7; game_map[1][2]=8;
array [Y][X]
game_map[2][4]; |
X direction ► |
| Y direction▼ |
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
| 6 |
7 |
5 |
0 |
Here is what the above 2D game map array will look like if you decided to
initialize it during declaration.
char game_map[10][10] = {{'X', 'X', 'X', 'X', 'X', 'X', 'X', 'X', 'X', 'X'},{'X', 'H', ' ', ' ', ' ', ' ', ' ', ' ', ' ', 'X'},{'X', ' ', ' ', ' ', ' ', ' ', ' ', ' ', ' ', 'X'},{'X', ' ', ' ', ' ', ' ', ' ', ' ', ' ', ' ', 'X'},{'X', ' ', ' ', ' ', ' ', ' ', ' ', ' ', ' ', 'X'},{'X', ' ', ' ', ' ', ' ', ' ', ' ', ' ', ' ', 'X'},{'X', ' ', ' ', ' ', ' ', ' ', ' ', ' ', ' ', 'X'},{'X', ' ', ' ', ' ', ' ', ' ', ' ', ' ', ' ', 'X'},{'X', ' ', ' ', ' ', ' ', ' ', ' ', ' ', ' ', 'X'},{'X', 'X', 'X', 'X', 'X', 'X', 'X', 'X', 'X', 'X'}};
The first index accesses the rows in the array, the second one accesses the
columns. Dimensions more than 2 gets difficult to work with. As far as
initializing a 3 or more dimensional array goes, you usually only see them
assigned values using a series of nested for loops. Here is a simple example.
//loop through first dimension
for (i = 0; i < 10; i++) { //loop through second dimension
for (j = 0; j < 10; j++) { //loop through third dimension
for (k = 0; k < 10; k++)
int_array[i][j][k]) = i * j * k;
}
}
Accessing Elements in Multidimensional Arrays
To access elements in a multidimensional array, all you have to do is provide
a combination of index values for each dimension to reach the desired element,
just like a bunch of cells in a spreadsheet or coordinates in a n dimensional
matrix or graph.
array_name[dim1_index][dim2_index] ... [dimn-1_index];
Setting values in a multidimensional array is just as simple as in a basic
array, you need to add another index per dimension.
array_name[index1][index2] ... [index s-1] = value;
Let’s return to our game_map 2d array for an example of setting a value in a
multidimensional array. We could position our hero character in the game_map
array using this snippet:
That would insert the character ‘H’ at the intersection of the cell found at
coordinate pair (1, 1) in the array.
Here we will look at retrieving a value from a multidimensional array using the
above syntax. If we wanted to print out our game level map we declared earlier
so that it gets displayed in the console we would use the following group of
nested for loops to go through both dimensions and print every value we
encounter.
for (i = 0; i < 10; i++) { for (j = 0; j < 10; j++) { printf("%c", game_map[i][j]); }
}
The first for loop goes through the index values from 0 to 9 of the first
dimension of the 2d array. The second for loop does the same for the second
dimension. We use the stdio built-in printf function to print the char (“%c”)
found at the coordinate pair (i, j). because of the nested loops, this code will
print every value in the 2d array game_map out to the console from indexes (0,
0) through (9, 9).
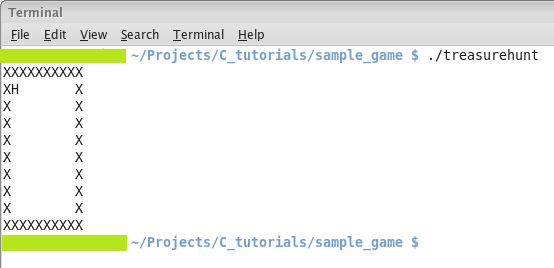
Sample Program
The code provided below defines a level in a treasure hunting game. It shows
how to declare and initialize both single and multi-dimensional array. The code
shows how to access and index of each element using a for loop.
//Treasure Hunter
//Very simple example C programming game.
//Example snippet for illustrating use of arrays.
#include <stdio.h>
void main(void) { int i, j;
char hero = 'H';
//Declares an array with 2 elements and initializes it.
char obstacles[3] = {'X', ' ', 'T'};
//Declare and initialize a 2 dimensional array of 10 rows and 10 columns.
//The use of obstacles array in the first column is just as an example of how
//to access the value of an array.
char game_map[10][10] = { {'X', 'X', 'X', 'X', 'X', 'X', 'X', 'X', 'X', 'X'}, {obstacles[0], ' ', ' ', ' ', ' ', ' ', ' ', ' ', ' ', 'X'}, {obstacles[0], ' ', ' ', ' ', ' ', ' ', ' ', ' ', ' ', 'X'}, {obstacles[0], ' ', ' ', ' ', ' ', ' ', ' ', ' ', ' ', 'X'}, {obstacles[0], ' ', ' ', ' ', ' ', ' ', ' ', ' ', ' ', 'X'}, {obstacles[0], ' ', ' ', ' ', ' ', ' ', ' ', ' ', ' ', 'X'}, {obstacles[0], ' ', ' ', ' ', ' ', ' ', ' ', ' ', ' ', 'X'}, {obstacles[0], ' ', ' ', ' ', ' ', ' ', ' ', ' ', ' ', 'X'}, {obstacles[0], ' ', ' ', ' ', ' ', ' ', ' ', ' ', ' ', 'X'}, {'X', 'X', 'X', 'X', 'X', 'X', 'X', 'X', 'X', 'X'}, };
//Place our hero at position 1,1 on the map.
game_map[1][1] = hero;
//Print the whole 2d array.
//loop through first dimension
for (i = 0; i < 10; i++) { //loop through second dimension
for (j = 0; j < 10; j++) { //print each array element.
printf("%c", game_map[i][j]); }
//Add newline at end to ensure each row gets printed correctly.
printf("n"); }
}
When you compile and run the above program, you will see output as shown
below:
[catlist id=170].