In this C++ tutorial, you will learn about pure virtual functions, declaration of a pure virtual function and virtual base class, virtual base class and how to implement a virtual base class, explained with examples.
What is a Pure Virtual Function:
A Pure Virtual Function is a Virtual function with no body.
Declaration of Pure Virtual Function:
Since pure virtual function has no body, the programmer must add the notation =0 for declaration of the pure virtual function in the base class.
General Syntax of Pure Virtual Function takes the form:
class class_name //This denotes the base class of C++ virtual function
{public:
virtual void virtualfunctioname() = 0 //This denotes the pure virtual function in C++
};
The other concept of pure virtual function remains the same as described in the previous section of virtual function.
To understand the declaration and usage of Pure Virtual Function, refer to this example:
#include <iostream>using namespace std;
class Exforsys{public:
virtual void example()=0; //Denotes pure virtual Function Definition
};
class Exf1:public Exforsys
{public:
void example()
{cout << "Welcome";
}};
class Exf2:public Exforsys
{public:
void example()
{cout << "To Training";
}};
void main()
{Exforsys* arra[2];
Exf1 e1;Exf2 e2;arra[0]=&e1;
arra[1]=&e2;
arra[0]->example();
arra[1]->example();
}
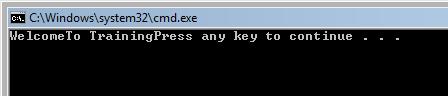
Since the above example has no body, the pure virtual function example() is declared with notation =0 in the base class Exforsys. The two derived class named Exf1 and Exf2 are derived from the base class Exforsys. The pure virtual function example() takes up new definition. In the main function, a list of pointers is defined to the base class.
Two objects named e1 and e2 are defined for derived classes Exf1 and Exf2. The address of the objects e1 and e2 are stored in the array pointers which are then used for accessing the pure virtual function example() belonging to both the derived class EXf1 and EXf2 and thus, the output is as in the above example.
The programmer must clearly understand the concept of pure virtual functions having no body in the base class and the notation =0 is independent of value assignment. The notation =0 simply indicates the Virtual function is a pure virtual function as it has no body.
Some programmers might want to remove this pure virtual function from the base class as it has no body but this would result in an error. Without the declaration of the pure virtual function in the base class, accessing statements of the pure virtual function such as, arra[0]->example() and arra[1]->example() would result in an error. The pointers should point to the base class Exforsys. Special care must be taken not to remove the statement of declaration of the pure virtual function in the base class.
Virtual Base Class
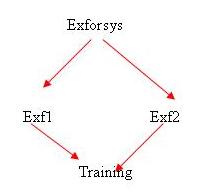
In the above example, there are two derived classes Exf1 and Exf2 from the base class Exforsys. As shown in the above diagram, the Training class is derived from both of the derived classes Exf1 and Exf2. In this scenario, if a user has a member function in the class Training where the user wants to access the data or member functions of the class Exforsys it would result in error if it is performed like this:
class Exforsys{protected:
int x;
};
class Exf1:public Exforsys
{ };
class Exf2:public Exforsys
{ };
class Training:public Exf1,public Exf2
{public:
int example()
{return x;
}};
The above program results in a compile time error as the member function example() of class Training tries to access member data x of class Exforsys. This results in an error because the derived classes Exf1 and Exf2 (derived from base class Exforsys) create copies of Exforsys called subobjects.
This means that each of the subobjects have Exforsys member data and member functions and each have one copy of member data x. When the member function of the class Training tries to access member data x, confusion arises as to which of the two copies it must access since it derived from both derived classes, resulting in a compile time error.
When this occurs, Virtual base class is used. Both of the derived classes Exf1 and Exf2 are created as virtual base classes, meaning they should share a common subobject in their base class.
For Example:
class Exforsys{protected:
int x;
;class Exf1:virtual public Exforsys
{ };
class Exf2:virtual public Exforsys
{ };
class Training:public Exf1,public Exf2
{public:
int example()
{return x;
}};
In the above example, both Exf1 and Exf2 are created as Virtual base classes by using the keyword virtual. This enables them to share a common subobject of their base class Exforsys. This results in only one copy that the member function example() of Class Training can access the member data x.
[catlist id=165].
