In this C++ Tutorial you will learn about the concepts of function – What is a function?, Features of a Function, Declaring a Function, Defining a function and Calling the function.
What is a function?
A function is a structure that has a number of program statements grouped as a unit with a name given to the unit. Function can be invoked from any part of the C++ program.
Features of Function:
To understand why the program structure is written separately and given a name, the programmer must have a clear idea of the features and benefits of function. This will encourage better understanding of function usage:
- Use of Functions gives a Structured Programming Approach
- Reduces Program Size:
The piece of code that needs to be executed, or the piece of code that is repeated in different parts of the program, can be written separately as a function and stored in a place in memory. Whenever and wherever needed, the programmer can invoke the function and use the code to be executed. Thus, the program size is reduced.
Having known about the function and its features let us see how to declare, define and call a function in a C++ program.
Declaring a Function:
It has been discussed that, in order for a variable to be used, it must be declared. Just like variables, it follows that function definitions must be declared. The general method of declaring a function is to declare the function in the beginning of the program.
The general format for declaring a function is
return_datatype function_name(arguments);
Suppose we have a function named as exforsys which returns nothing from the function it is declared as
void exforsys( );
This declared would inform the compiler that the presence of the function exforsys is there in the program. In the above the return type void tells the compiler that the function has no return value and also the empty braces ( ) indicate that the function takes no arguments.
Defining a function:
The definition is the place where the actual function program statements or in other words the program code is placed.
The general format of the function definition is as follows:
return_datatype function_name(arguments) //Declarator
{program statements //Function Body...
...
}
In the above the declaration must match the function declaration already made. That is the function name, the return type and the number of arguments all must be same as the function declaration made. In fact, if arguments are declared and defined, the order of arguments defined here must match the order declared in the function declaration.
After the declaration, the braces starts and the function body is placed. The function body has the set of program statements which are to be executed by the function. Then the function definition ends with “}” ending braces.
For example let us see how to define a function exforsys declared as void that prints first five integers.
void exforsys( )
{int i;
for (i=1;i <= 5;i++)
cout<< i;
}};
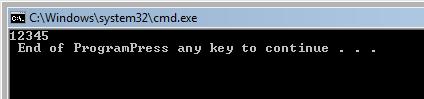
The output of the function when it is called would be
12345Calling the function:
The function must be called for it to get executed. This process is performed by calling the function wherever required.
The general format for making the function call would be as follows:
functionname();
When the function is called the control, transfers to the function and all the statements present in the function definition gets executed and after which the control, returns back to the statement following the function call.
In the above example when the programmer executes the function exforsys, he can call the function in main as follows:
exforsys();
Let us see a complete program in C++ to help the programmer to understand the function concepts described above:
#include <iostream>using namespace std;
void main( )
{void exforsys( ); //Function Declaration
exforsys( ); //Function Called
cout << "n End of Program";
}void exforsys( ) //Function Definition
{int i;
for(i=1;i<=5;i++)
cout<< i;
}
The output of the above program is
[catlist id=165].
