In object-oriented programming language, whenever a block of statements has to be repeated a certain number of times or repeated until a condition becomes satisfied, the concept of looping is used.
The following commands used in C++ for achieving looping:
- for loop
- while loop
- do-while loop
for loop:
The syntax of for loop is
for (initialization; condition; increase or decrease)
{statement block;}
Initialization is the primary value set for a variable. Initialization is only executed one time. After initialization is performed, it is not executed again. The condition specified is checked and if the condition returns a value of true, (if the condition is satisfied), the loop is continued for execution. If the condition returns a value of false, (the condition is not satisfied), then the statements following the loop block are not executed and the control is transferred to the end of the loop. The statement specified in the for loop can be a statement block or more than one statement. These statements must be enclosed within flower brace symbols{ }. The statement block can also be a single statement. For a single statement, the flower brace symbols are not needed and may be specified as:
for (initialization; condition; increase or decrease)
statement;
If the condition becomes satisfied, all the statements in the for block are executed, the increase or decrease is executed on the variable and again the condition is checked, so the loop continues with these commands until the condition becomes false.
It is important for the programmer to remember that the optional attributes are initialization and increase/decrease where the for loop must be written as:
for (;condition;)
or as
for(initialization ; condition;)
It is also possible to initialize more than one variable in a for loop and to perform this the programmer uses the comma operator denoted as “,”.
For example:
To initialize two variables namely a and b with value 5 and 10 respectively and increment a and decrement b this can be done as follows;
for (a=5,b=10;a!=b; a++, b--)
Let us see a small example using for loop:
#include <iostream>using namespace std;
void main()
{for (int x=5; x>0; x--)
{cout << x << "; ";
}cout << "EXFORSYS";
}
The output of this program is
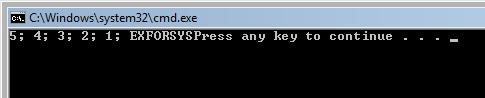
while loop:
Statement of while statement is:
while (expression)
{statement block;}
Until the condition represented in the expression is true (satisfied), the set of statements in while block is executed. As in for loop, when the number of statements to be executed is more than one (if the condition is satisfied), then it is placed inside the flower braces as shown in the example above. If the number of statements to be executed is one, if the condition is satisfied, then the flower braces may be removed.
For Example:
#include <iostream>using namespace std;
void main ()
{int x;
cout << "Input the number:";
cin >> x;
while (x>0)
{cout << x << "; ";
--x;
}cout << "EXFORSYS";
}
Here the output of the above program is

In this example, the input number is 5 and the while loop is executed starting from 5 until the number reaches a value <0.Whilethe value of x>0 the statement inside the while block prints the value of x. When this is completed, the numbers 5, 4, 3, 2, 1 are printed. After the value of x reaches less than zero, the control passes to outside the while block and EXFORSYS is printed.
do-while loop:
The syntax of do-while loop is
do{statement block;} while (condition);
The do while loop functionality is similar to while loop. The main difference in do-while loop is that the condition is checked after the statement is executed. In do-while loop, even if the condition is not satisfied the statement block is executed once.
For Example:
Suppose a programmer wishes to output the input number until the user types the number 5. This can be done using a do..while loop structure as follows:
#include <iostream>using namespace std;
void main ()
{int x;
do{cout << "Input the number:";
cin >> x;
cout << "The number is:" << x << "n";
} while (x != 5);
cout << "End of program";
}
The output of the above program is:
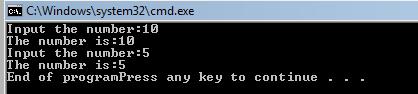
[catlist id=165].
