In this C++ tutorial you will learn about Operator Overloading in two Parts, In Part I of Operator Overloading you will learn about Unary Operators, Binary Operators and Operator Overloading – Unary operators.
Operator overloading is a very important feature of Object Oriented Programming. Curious to know why!!? It is because by using this facility programmer would be able to create new definitions to existing operators. In other words a single operator can take up several functions as desired by programmers depending on the argument taken by the operator by using the operator overloading facility.
After knowing about the feature of operator overloading now let us see how to define and use this concept of operator overloading in C++ programming language.
We have seen in previous sections the different types of operators. Broadly classifying operators are of two types namely:
- Unary Operators
- Binary Operators
Unary Operators:
As the name implies, it operates on only one operand. Some unary operators are named ++ also called the Increment operator, — also called the Decrement Operator, ! , ~ are called unary minus.
Binary Operators:
The arithmetic operators, comparison operators, and arithmetic assignment operators all this which we have seen in previous section of operators come under this category.
Both the above classification of operators can be overloaded. So let us see in detail each of this.
Operator Overloading – Unary operators
As said before operator overloading helps the programmer to define a new functionality for the existing operator. This is done by using the keyword operator.
The general syntax for defining an operator overloading is as follows:
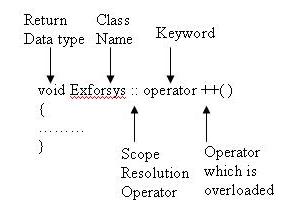
return_type classname :: operator operator_symbol(argument)
{...
statements;
}
Thus the above clearly specifies that operator overloading is defined as a member function by making use of the keyword operator.
In the above:
- return_type – is the data type returned by the function
- class name – is the name of the class
- operator – is the keyword
- operator symbol – is the symbol of the operator which is being overloaded or
- defined for new functionality
- :: – is the scope resolution operator which is used to use the function definition outside the class. The usage of this is clearly defined in our earlier section of How to define class members.
For example
Suppose we have a class say Exforsys and if the programmer wants to define a operator overloading for unary operator say ++, the function is defined as
Inside the class Exforsys the data type that is returned by the overloaded operator is defined as
class Exforsys{private:
...
public:
void operator ++( );
...
};
So the important steps involved in defining an operator overloading in case of unary operators are:
Inside the class the operator overloaded member function is defined with the return data type as member function or a friend function. The concept of friend function we will define in later sections. If in this case of unary operator overloading if the function is a member function then the number of arguments taken by the operator member function is none as seen in the below example. In case if the function defined for the operator overloading is a friend function which we will discuss in later section then it takes one argument.
The operator overloading is defined as member function outside the class using the scope resolution operator with the keyword operator as explained above
Now let us see how to use this overloaded operator member function in the program
#include <iostream>using namespace std;
class Exforsys{private:
int x;
public:
Exforsys( ) { x=0; } //Constructor
void display();
void operator ++( );
};
void Exforsys :: display()
{cout << "nValue of x is: " << x;
}void Exforsys :: operator ++( ) //Operator Overloading for operator ++ defined
{++x;
}void main( )
{Exforsys e1,e2; //Object e1 and e2 created
cout << "Before Increment";
cout << "nObject e1: "; e1.display();
cout << "nObject e2: "; e2.display();
++e1; //Operator overloading applied
++e2;
cout << "n After Increment";
cout << "nObject e1: "; e1.display();
cout << "nObject e2: "; e2.display();
}
The output of the above program is:
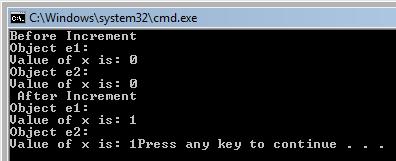
In the above example we have created 2 objects e1 and e2 f class Exforsys. The operator ++ is overloaded and the function is defined outside the class Exforsys.
When the program starts the constructor Exforsys of the class Exforsys initialize the values as zero and so when the values are displayed for the objects e1 and e2 it is displayed as zero. When the object ++e1 and ++e2 is called the operator overloading function gets applied and thus value of x gets incremented for each object separately. So now when the values are displayed for objects e1 and e2 it is incremented once each and gets printed as one for each object e1 and e2.
This is how unary operators get overloaded. We will see in detail how to overload binary operators in next section.
[catlist id=165].
