In this C++ tutorial, you will learn about string representation and handling, how a string is represented, end string notation, initializing char array, character representation, string literals, example program to understand the character array concept and the accessing of character array in detail and how to represent an array of Strings.
How is a string represented?
Strings, or sequences of characters, are represented as arrays of char elements. For example, when a programmer wants to represent a char array Exforsys having 30 elements it is declared:
char Exforsys[30];
This means the character array has 30 storage location allocated where it can store up to a maximum of 30 characters.
End String Notation
The character array can store the specified maximum of array limit. This means it can store less than the allocated array limit up to the maximum. It is essential that a notation exist to mark the end of character array or string representation. This end of character array is denoted using backslash zero ‘�’.
The Differences between Character Constants and String Literal:
Initializing Char array
Suppose the programmer wants to initialize the array char Exforsys[30] with value Training. This initialization of char array can be performed using two methods:
- Character representation
- String Literals
The character representation is notated as follows:
char Exforsys[30]= {‘T’,’r’,’a’,’i’,’n’,’i’,’n’,’g’,’�’};
The string literal representation is notated as follows:
char Exforsys[30]= “Training”;
Character representation uses single quotes to represent each character while string literal representation uses double quotes for the entire string literal.
Another main difference with character representation is the end of character denoted by ‘�’. String literal representation uses double quotes; there is no need for representing the end of character. The end of character task is automatically performed by C++ programming language.
It is also possible to initialize array as follows:
char Exforsys[ ]=”Company”;
In the above case, the char array Exforsys is not mentioned with the size and is initialized with the string literal Company. The character array Exforsys takes the size of the initialized string literal.
An Example:
Input string defined as character array with the same output on the display screen:
#include <iostream>using namespace std;
void main( )
{char Exforsys[80];
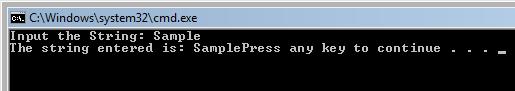
cout << "Input the String: ";
cin >> Exforsys;
cout << "The string entered is: " << Exforsys;
}
The output of the above program is
Detailed example to understand the concept of character array and accessing of character array:
The below example uses two input strings as two character arrays, accessing one character array character by character, then copies it into the other character array.
The output of the above program is
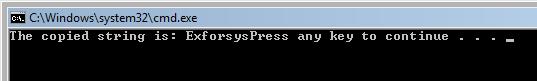
In the above program, the string function strlen is used. This string function is used to find the length of the string given in the argument of the function. In this case, it finds the length of the string Exforsys. This predefined special string function strlen is present in the header file string.h. Therefore, this is also included in the program.
In this example, the first string initializes with string literal Exforsys and the second literal declares as an empty string. The for loop uses the first character from the first character array examp1[] and copies it into the first position in the second character array examp2[]. The loop continues until the end of string value is reached. The second character array is terminated by end of character and then printed.
The above example provides the programmer with insight on how to declare character arrays, how to initialize character arrays and how to access character arrays.
The above example can also be performed using a predefined string function called strcpy.
The string function strcpy takes two strings as argument.
The general syntax is as follows:
strcpy(string1,string2);
The string function strcpy copies the string2 (the second argument) into string1 (the first argument).
How to represent array of Strings:
It is possible to declare two-dimensional arrays in character arrays or array of strings.
The general syntax is as follows:
char arrayname[numb1][numb2];
In this numb1 denotes the number of string literals defined in the array and numb2 defines the maximum length of characters of the strings.
For example, if the programmer wants to represent a char array Exforsys with string literals as:
Training
Forums
Program
Then numb1 takes the value 3 and numb2 takes the value 8 because Training has the maximum character 8. The representation is as follows:
char Exforsys[3][8];
The access of the character array can be performed by using for loop.
[catlist id=165].
