Since the release of Oracle 8.1.6, analytic functions have emerged as a major extended strength of SQL language. Analytic functions address the problems like moving averages, cumulative sums, ranking, percentile and many other problems which are crucial for OLAP applications. Such data operations are required for business applications which involve strategic decision making and predictive forecasts.
Topics
Analytic functions work with ordered grouped data sets or ‘windows’ which are created by the analytic clause. Each window constitutes a defined set of rows which satisfy defined conditions relative to the current row. Analytic function logic is operative upon this data set under the window. Some of the key accomplishments of SQL analytic functions are drawn in the below figure.
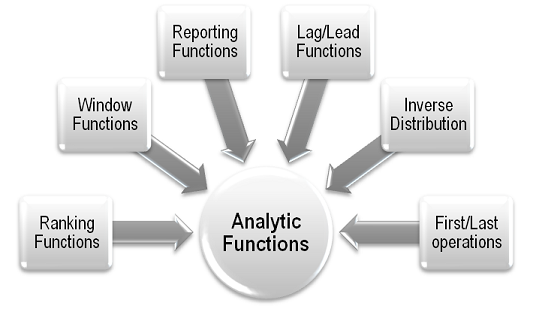
Analytic operations are processed as the last one in an unsorted query (without ORDER BY clause) execution process. Until Oracle 10g, the major and frequently used analytic functions are RANK, DENSE_RANK, LEAD, LAG, ROW_NUMBER, and RANGE. In addition to the analytic functions, several aggregate functions also reveal their analytic behavior in SELECT queries. Aggregate functions like MIN, MAX, and SUM can inherit analytic behavior when operated in a window.
In this article, we shall focus on the analytic enhancements in Oracle 11g. Oracle 11g introduced two new functions inSQL namely, LISTAGG and NTH_VALUE.
The LISTAGG function
Oracle 11g Release 2 included a new function in the aggregate cum analytic
functions category. The built in function is known as LISTAGG which can be used to aggregate string with a delimiter. The LISTAGG function not only aggregates
the strings but also puts them in a specified order.
Before digging into the details of LISTAGG function, let us understand the
string aggregation. We shall see the string aggregation in a group and in a row.
The below figure shows the sample order data for each month has been aggregated
month wise.
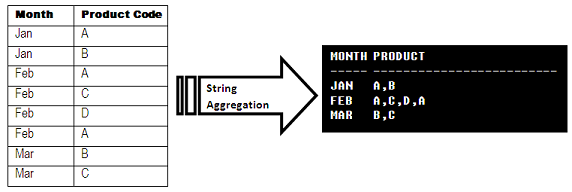
Prior to release of Oracle 11g, there were several workaround solutions to
achieve string aggregations as listed below
• STRAGG (currently it exists in SYS schema in unusable state)
• WM_CONCAT (exists in WMSYS user)
• User defined stored function or an aggregate function
• Workarounds using ROW_NUMBER and SYS_CONNECT_BY_PATH
• COLLECT function using object type table
In comparison to the above solutions, LISTAGG function is efficient in terms of performance and usage convenience.
The LISTAGG function follows the below syntax
LISTAGG( [ ]) WITHIN GROUP (ORDER BY ) [OVER (PARTITION BY )]
Note that the LISTAGG has mandatory WITHIN GROUP (ORDER BY) clause. Oracle raises exception if any of the clause is missing while using LISTAGG in queries.
The aggregate behavior of LISTAGG can be extended by adding the windowing clause OVER (PARTITION BY).
Aggregate behavior of LISTAGG
The aggregate behavior of the LISTAGG function is quite straightforward and goes exactly as the purpose. The function simply aggregates the column values which fall under the group. Sorting of the aggregated string depends upon the ORDER BY specification. If no sorting criterion has to be applied, NULL can be specified. Let us check both the cases and observe the difference.
We shall demonstrate the illustration on the EMPLOYEES table. The SELECT query below aggregates the employee names which have the same job category.
SELECT job, LISTAGG( ename, ‘,’) WITHIN GROUP (ORDER BY NULL) names FROM employees GROUP BY job /

Now let us check the difference by setting the order of the above output. We will sort the names in ascending order of their hire date.
SELECT job, LISTAGG( ename, ‘,’) WITHIN GROUP (ORDER BY hiredate) names FROM employees GROUP BY job /

Thus, we see the effect of ORDER BY clause in the LISTAGG function. The aggregate behavior of the function can be easily and frequently employed to resolve string aggregation problems.
Analytic behavior of LISTAGG
Till now, we examined the aggregate side of the LISTAGG function. The LISTAGG function shows analytic behavior when used with OVER() clause. Let us illustrate a small example
The query below demonstrates the analytic behavior of LISTAGG function. The window is created by the JOB column. Note that the output of LISTAGG function is same for the complete window. This deduces the fact that analytic function output moves for each row of its window, which is not the case in aggregate functions.
SELECT job, ename, sal, LISTAGG (ename, ‘,’) WITHIN GROUP (ORDER BY sal) OVER (PARTITION BY job) names FROM employees /
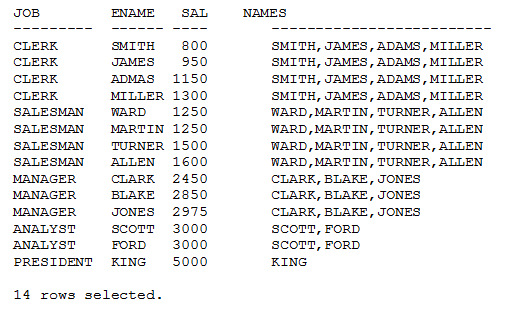
The NTH_VALUE function
Since Oracle 9i Release 2, we have been using the FIRST_VALUE and LAST_VALUE
analytic functions in SQL. While the FIRST_VALUE retrieves the first value of a column in a window which contains partitioned data in ordered way. Similarly, the LAST_VALUE
function gives the last value of the window. For random selection in a window, programmers used a workaround solution.
Oracle 11g R2 introduces a new analytic function with similar genre. The NTH_VALUE function can pick a random record from the window. Not only first or last, the function can pull out fifth, tenth or any specific value from the data set.
The NTH_VALUE function has the below syntax
NTH_VALUE (, ) [FROM FIRST | FROM LAST] [RESPECT NULLS | IGNORE NULLS] OVER (PARTITION BY ORDER BY )
In the above syntax, [FROM FIRST | FROM LAST] is an optional clause which determines whether the operation has to start from first row or last row. By default, it is FROM FIRST.
[RESPECT NULLS| IGNORE NULLS] clause determines whether NULL values are to be included or excluded in the calculation. By default, it is RESPECT NULLS.
The OVER()clause creates the window for the analytic operation.
Analytic behavior of NTH_VALUE function
We shall illustrate the analytic applications of NTH_VALUE function in the below examples.
Very often we come across the scenarios where we need to retrieve the second highest salary drawer in each job category. Using sub queries and multiple analytic functions, it used to be a cumbersome workaround solution. Let us observe how NTH_VALUE function simplifies the solution.
SELECT job, ename,sal, NTH_VALUE (sal,2) OVER (PARTITION BY job ORDER BY sal DESC) SECOND FROM employees ORDER BY job, sal DESC /
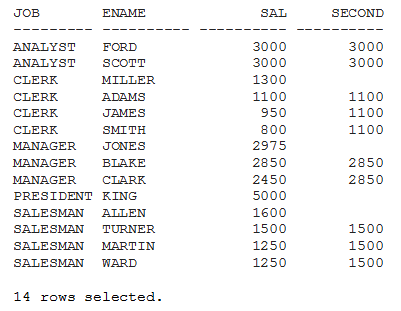
In the above output, note the second highest salary in each job category; Adams is the second highest paid clerk while Blake is the second highest paid manager.
Comparing NTH_VALUE against its predecessors FIRST_VALUE and LAST_VALUE, the
function can well derive its predecessors too. NTH_VALUE (column, 1) FROM FIRST is equivalent to FIRST_VALUE while NTH_VALUE (column, 1) FROM LAST is equivalent to LAST_VALUE.
Conclusion
The article describes the aggregate and analytic enhancements made in Oracle 11g. With the new inductions, previously practiced workaround solutions would surely be relieved off. I hope my efforts to describe the usage and applications of the functions would be fair and considerable.
[catlist id=185].