In this C++ tutorial, Structures Part II, you will learn how to use structure in an efficient way, and features of structures explained with examples.
Structure Members Initialization:
As with arrays and variables, structure members can also be initialized. This is performed by enclosing the values to be initialized inside the braces { and } after the structure variable name while it is defined.
For Example:
#include <iostream>using namespace std;
struct Customer{int custnum;
int salary;
float commission;
};
void main( )
{Customer cust1={100,2000,35.5};
Customer cust2;cust2=cust1;
cout << "n Customer Number: "<< cust1.custnum << "; Salary: Rs."<< cust1.salary << "; Commission: Rs." << cust1.commission;
cout << "n Customer Number: "<< cust2.custnum << "; Salary: Rs."<< cust2.salary << "; Commission: Rs." << cust2.commission;
}
The output of the above program is
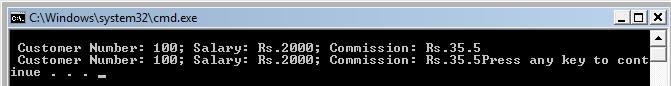
In the above example, the structure variable can be assigned to each by using assignment operator ‘=’. The programmer must consider that only structure variables of the same type can be initialized. If a programmer tries to initialize two structure variables of different types to each other it would result in compiler error.
It is wrong to initialize as:
Customer cust1;cust1= {100,2000,35.5};
Nesting of structures:
Nesting of structures is placing structures within structure. How to declare nesting of structures? How to access structure members in case of nesting of structures?
For Example:
#include <iostream>using namespace std;
struct course{int couno;
int coufees;
};
struct student{int studno;
course sc;course sc1;};
void main( )
{student s1;s1.studno=100;
s1.sc.couno=123;
s1.sc.coufees=5000;
s1.sc1.couno=200;
s1.sc1.coufees=5000;
int x = s1.sc.coufees + s1.sc1.coufees;
cout<< "n Student Number: "<< s1.studno <<"n Total Fees: Rs."<< x;
}
The output of the above program is
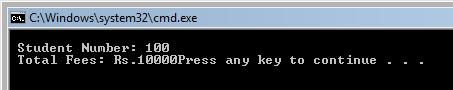
In the above example, the structure course is nested inside the structure student. To access such nested structure members, the programmer must use dot operator in the above case twice to access the nested structure members.
In the above example:
s1.sc.couno
s1 is the name of the structure variable, sc is the member in the outer structure student. couno is the member in the inner structure course. This is how nested structure members are accessed.
One more important feature of C++ structure is it can hold both data and functions. This is in contrast to C where structures can hold only data. Though C++ structures can hold both data and functions, most classes are used for the purpose of holding both data and functions and structures are used to hold data.
[catlist id=165].
