Introduction: We all talk about webservices, webservices can do this and webservices can do that. But when we are asked to make one, we hesitate. Maybe it’s because we never made a webservice before, and all the time playing with Webforms and Windows Forms or even Console Applications. By the way, I love Console applications. In this article, I will show you how to create a simple webservice that is consumed by a Console application client.
Motivation of the XML Web Services
Most of the people does not understand that why we need a web service and make a wrong use of it. The main idea of a web service is to join two businesses together since they cannot join due to their graphical locations. Web Service is also used to link different systems together. The best thing about this is that the systems can be in different in nature. Meaning a web service enables a windows application to interact and communicate with the linux application. This is done by using XML as the transferring medium. Since XML is understood by all the systems because its nothing but plain text that’s why this is a perfect language to join systems together. XML web Service should never be used to transfer confidential data, not to be used in real time programming where time is the essence.
Making the Web Service
First, start your Visual Studio .NET, and in the project type, select ASP.NET WebService. In the left pane, choose the language of your choice. In this example, I will be using Visual C#.NET. Once you select the project, a page will appear which will be more like a design page, switch to its code view. In the code view, you can see lot of comments and C# code already written for you. You will also see that at the bottom, there is a method HelloWorld which is written for you by default, so you can test your service and of course say hello to the world. After removing the unwanted code and comments, your code will look like this:
using System; using System.Collections; using System.ComponentModel; using System.Data; using System.Diagnostics; using System.Web; using System.Web.Services; namespace WebServiceExample { public class Service1 : System.Web.Services.WebService { public Service1() { InitializeComponent(); } // Add the Description Attribute so you // will know the purpose of your WebService [WebMethod(Description="This Method prints HelloWorld")] public string HelloWorld() { return "Hello World"; } } }
Let’s dig into this small code. [WebMethod] Attribute denotes that this method will be used by the clients, also this method has to be public in order for a client to use it. Description inside the WebMethod Attribute just gives the method more meaning. Don’t worry about the InitializeComponent() method since it’s written by default.
Running the Web Service
OK, now you have made your first kick ass WebService (without even writing a single line of code). Let’s run it and check whether it gives the correct result or not. In the Solution Explorer, right click on the .asmx file, and select View in Browser as shown below:
Once you click on “View in Browser”, the next screen you will see will be something like this:

have erased most of the stuff, so you can only see the method that you need in this example. Below, you can see the method HelloWorld and the description you wrote for the method.
Now, click on the HelloWorld method. I don’t want to scare you with all the SOAP and HTTP code produced, so I am only going to paste the screen shot which will be relevant to this example.
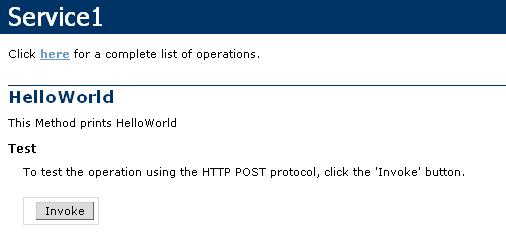
Alright, so far so good. Now, just press the Invoke button to see the result of your method named HelloWorld().
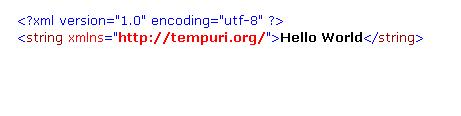
This is cool. You have just tested your first webservice and it ran since you didn’t coded it. I know what you are thinking right now. Is the client going to see the result like this strange format (this is XML format). Well, of course not. That’s why you need to make a Proxy class which consumes this service.
{mospagebreak}
Making the Web Service Client
Let’s make a Console application which consumes this service. You can use any language and platform to consume this service, that’s the purpose of XML WebService. Now, this procedure requires some mouse clicking :). So I will write down the steps instead of pasting the screen shots.
- Start a new project which will be a Console Application in Visual C#.NET.
- Once you see the code view in the Console application, right click on the project name from the Solution Explorer. Remember that project name will be written in bold.
- Click on “Add Web Reference”.
- Paste the URL of your WebService. You can get the URL of your WebService when you view your webservice in IE or any other browser.
- Click GO.
- Your webservice will be loaded. In the Web Reference Name textbox, write “MyService” and click Add Reference.
- You will see that the web reference has been added in your Solution Explorer, meaning that webservice is ready to kick some butt.
Now, all you have to do is to make the instance of the WebService class using the reference name that you provided, which is “MyService”.
using System;
namespace MyClient
{
class Class1
{
[STAThread]
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// Make an instance of the WebService Class
// using the Web Reference you provided
MyService.Service1 service = new MyService.Service1();
// Assign message what ever is returned
// from HelloWorld in this case “HelloWorld”
string message = service.HelloWorld();
// Prints out the message on the screen
Console.WriteLine(message);
}
}
}
And that’s it. You use the webservice class just like any other class. Something you need to keep in mind is that if you decide to make a new method in your webservice and want to make it available to the client, then always remember to build your webservice solution so that the assembly can be updated. If you don’t build your webservice, you won’t be able to see the methods on the client side.
Http Clients Creating .NET Consumers
A consumer is the one who uses the service and a provider is the one who provides the service. Http clients can be an asp.net application or any other application that communicates with the web service through internet.
Web Services and Legacy Clients
As I said previously that Web Services are used to communicate between different systems. These systems can be writting different operating systems but their communication medium is xml which they all can understand. These legacy systems can be COBOL, FORTON and PASCAL. So instead of making a complete new application in Asp.net Web Service can be used to link different systems together.
[catlist id=174].