J2EE Overview
J2EE is a technology that aims to simplify the design and implementation of enterprise applications. In this tutorial you will learn what J2EE is, its benefits, J2EE main components, Evolution of Enterprise Application Frameworks, Why use J2EE, J2EE Platform Architecture, J2EE APIs and Technologies and J2EE Reference Implementation. Before continuing our J2EE discussion lets define what an enterprise application is.
Enterprise application is an application which probably has legacy existing applications and databases that you want to continue using them while adding or migrating to a new set of applications that exploit Internet, e-commerce and other new technologies.
Evolution of Enterprise Application Frameworks
The main reasons for the evolution of enterprise application frameworks are listed below:
• Need to attune new technologies especially improvements on web technologies
• Need to handle complex low level details inherent in enterprise applications like security, transaction processing and multi-threading.
• Evolution and popularity of widely accepted concepts like n-tier architectures and component based software development.
Several enterprise application frameworks have emerged based on the above listed needs. Some of the best known examples are Java2 Platform Enterprise Edition (J2EE) from Sun Microsystems, Distributed internet Applications Architecture (DNA) from Microsoft and Common Object Request Broker Architecture (CORBA) from Object Management Group (OMG).
Why use J2EE
J2EE may not be the perfect choice for developing enterprise applications. You should consider other alternatives before deciding to use J2EE. Some advantages of using J2EE for enterprise applications are listed below:
• Low level services are already implemented
An enterprise application needs to implement very complex services to be successful. Some of those services are transaction and state management, resource pooling and multi-threading. J2EE architecture separates those low level services from the application logic. Since all those services are implemented by applications servers, you can save a lot of time if you need those services.
• J2EE is well documented and understood
J2EE is developed by a consortium formed by several major companies in the industry. For more information on this consortium you can search for “Java Community Process” (see links section)
• J2EE is a standardized and reliable software architecture
Using standardized and reliable software architecture in your development will most likely decrease your future costs and ensure longevity of your applications.
• J2EE gives you a lot of flexibility
Once you develop your application with J2EE, you can deploy it wherever you need to. You can deploy your application to any application server with small changes.
• APIs used in J2EE are well documented.
Several APIs are used to implement low level details of enterprise applications. Since those APIs are already written and well documented, this will save you a lot of time.
J2EE Platform Architecture
J2EE platform uses a multi-tiered distributed application model. Application logic is divided into components and each component is installed on a specific machine based on which tier that component resides.
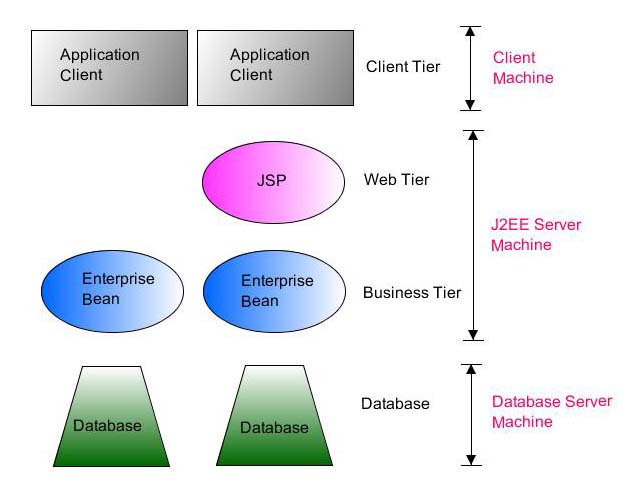
Figure-1 J2EE Application Model
As you can see from the Figure-1, there are four tiers in J2EE application model: client tier, web tier, business tier and enterprise information system (EIS) tier. Business and web tiers are generally existed in a server application called application server or J2EE server. Application server provides complex services needed by components in business and web tiers.
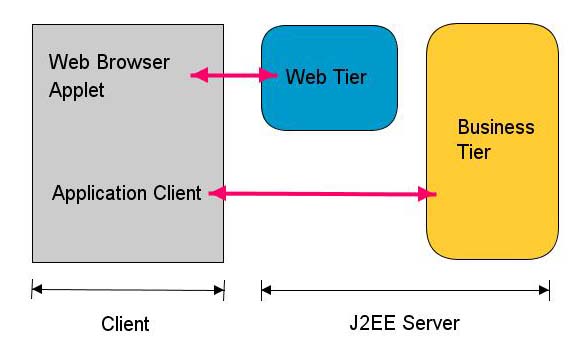
Figure-2 Interaction between client, web and business tiers in J2EE
Client tier can have two types of components: web client or application client. Web clients access the components in the web tier namely servlets or java server pages (jsp). Web browsers as a web client are generally used to access web tier components.
Application clients are standalone applications that do not run in browsers (e.g. swing application). They directly accesses to the components in the business tier.
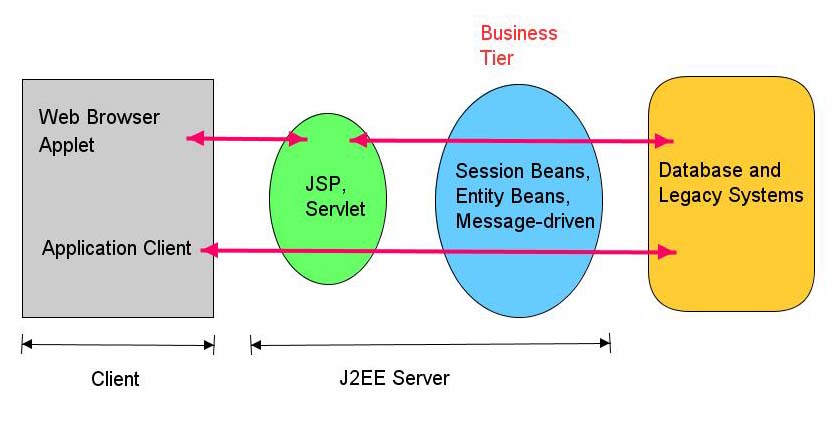
Figure-3 Business and EIS tiers
Figure-3 shows Business and EIS tiers in detail. EIS tier contains database and legacy systems and can be accessed from the business tier.
There are three types of components in business tier: entity beans, session beans and message-driven beans. We will discuss them separately in detailed subsequent tutorials.
Another important concept in J2EE architecture is the “container” concept. An enterprise application needs to implement very complex services to be successful. Some of those services are transaction and state management, resource pooling and multi-threading. J2EE architecture separates those low level services from the application logic by implementing those services in containers. So, web containers are mainly used to provide low level services to web components (e.g. servlet) or EJBs (e.g. entity beans) Containers are also used to manage execution of the components in business tier. Figure-4 may demystify this idea more.
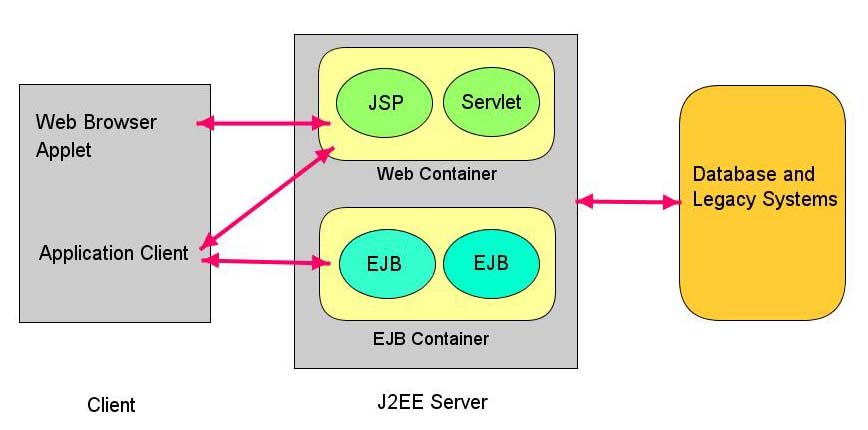
Figure-4 J2EE Application Server and Containers
J2EE APIs and Technologies
There are several APIs and technologies which make J2EE a working platform. These APIs and technologies are described below briefly:
1. Java Database Connectivity (JDBC) API: JDBC is a set of interfaces which allows Java applications access to any database. This API has the same purpose as Microsoft’s ODBC.
2. Remote Method Invocation (RMI): RMI is an API which allows Java objects to communicate remotely with other objects. This API has the same purpose of CORBA from OMG.
3. Java IDL: IDL is a standard platform-independent declarative language which is used to define interfaces that object implementations provide and client objects call. Java IDL allows any Java object to communicate with other objects in any language by means of IDL.
4. Enterprise Java Beans: EJB is a standard distributed object framework and component model to Java. Enterprise Java Beans are components used in business tier of J2EE. The details and types of EJBs will be discussed in subsequent tutorials.
5. Servlets and Java Server Pages (JSP): Servlets are Java programs running on a web server and that produces results viewed remotely on a web server. Servlets and JSPs have the same purpose that CGI or PHP had in the past.
6. Java Message Service (JMS): JMS API is a messaging standard that allows J2EE components to create, send, receive, and read messages. It enables distributed communication between components.
7. Java Transaction API (JTA): JTA allows J2EE components to perform distributed transactions. Distributed transaction processing is a complex topic which is out of scope of this tutorial.
8. JavaMail: JavaMail API allows Java components send and receive emails in a platform-independent way.
9. Java API for XML Processing (JAXP): Extensive Markup Language (XML) is a data format for interchanging structured documents on the Web. JAXP allows Java applications to parse and transform XML documents. XML is heavily used in J2EE as a data format.
10. Java Naming and Directory Interface (JNDI): JNDI is a protocol which provides a standard API to access naming and directory services. Naming and directory services associate names with locations, services, information and resources. So, JNDI allows Java applications to find any necessary resource in a standard way.
J2EE Reference Implementation
J2EE reference implementation is the implementation of J2EE model described in the previous sections. It is freely available on the website of Sun. (see the links section) It includes Sun’s J2EE Application Server, a J2EE-compatible product for developing and deploying J2EE applications plus related development tools and documentation.
J2EE reference implementation is probably the best starting point for developing enterprise applications. But if you just plan to use web tier components (e.g. servlet and jsp), we recommend you to start with Tomcat.
Links
·J2EE Reference Implementation
· J2EE Tutorial
· J2EE API Documentation
· J2EE 1.4 Specification
· Tomcat
· Java Community Process
· JDBC Technology Homepage
· RMI Technology Homepage
· Java IDL Technology Homepage
· EJB Technology Homepage
· Servlet Technology Homepage
· JMS Technology Homepage
· JTA Technology Homepage
· JavaMail API Homepage
· JAXP Homepage
· JNDI Technology Homepage
[catlist id=173].
