Servlet Basics
Servlets are Java programs running on a web server that produce results viewed remotely on a web server. Servlets has the same purpose that CGI or PHP had in the past. We shall describe how Servlets works with some examples. You will also learn about Servlet Request and Response Model, Servlet Life Cycle, Servlet Scope Objects and Error Handling.
Servlet Request and Response Model
Note that although there are two types of servlets (GenericServlet and HttpServlet), we will discuss here only HttpServlet since GenericServlet can be used for advanced needs. The important thing here is that you should use GenericServlet if you want your servlet to response in another protocol rather than HTTP.
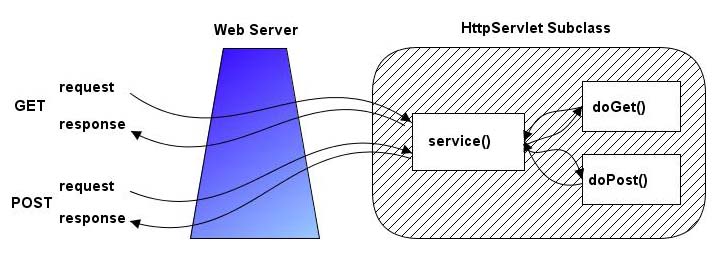
Figure-1 Request and Response Model of HttpServlets
HttpServlets are servlets that respond to the HTTP protocol requests which is used by web servers to return us the requested web pages. We need to extend javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet class to write a servlet. We should select one of doGet or doPost methods for overriding. This choice depends on what type of http request (GET request or POST request) we are expecting. GET request is generally only used to retrieve data from the web server, however POST request are used for more complex requests like storing data. We will generally override both methods in our tutorials and call a processRequest method to handle both types of request.
Let’s start with our first servlet which is called HelloWorld1 servlet. HelloWorld1 servlet will just print “Hello World1” message.
|
The source code shown in this section can be found in HelloWorld1 project. |
Figure-2 shows overridden doGet and doPost methods in our HelloWorld1 servlet. Both methods call processRequest method to handle the http requests. Figure-3 shows processRequest method.
|
/** Handles the HTTP < code >GET< /code > method. protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, /** Handles the HTTP < code >POST< /code > method. * @param request servlet request * @param response servlet response */ protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) |
Figure-2 Overridden doGet and doPost methods in HelloWorld1 servlet
|
public class HelloWorld1 extends HttpServlet { /** Processes requests for both HTTP < code >GET< /code > and < code >POST< /code > methods. * @param request servlet request * @param request servlet response */ . .....throws ServletException, IOException { .....response.setContentType(“text/html;charset=UTF-8”); ..........PrintWriter out = response.getWriter(); ..........Out.println(“< html >”); ..........Out.println(“< head >”); ..........Out.println(“< title >Servlet HelloWorld1< /title >”); ..........Out.println(“< /head >”); ..........Out.println(“< body >”); ..........Out.println(“< h1 >HelloWorld1< /h1 >”); ..........Out.println(“< /body >”); ..........Out.println(“< /html >”); ..........Out.close(); } |
Figure-3 ProcessRequest method used in HelloWorld1 servlet
We get the PrintWriter object from HttpServletResponse object to write the contents of the html page to other side. After writing our content, we close the PrintWriter object. You will get a result similar to shown in Figure-4 after you run the project.
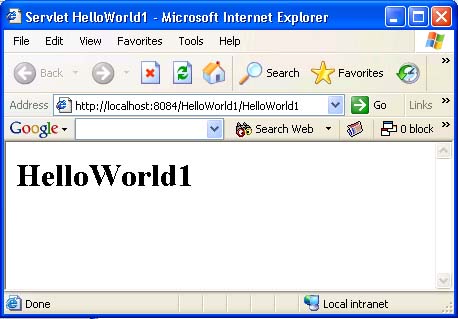
Figure-4 HelloWorld1 servlet running in a browser
Servlet Life Cycle
Servlet container creates only one instance of each servlet but the request of each user is handled with a separate thread. Each thread then calls doGet or doPost methods. This idea is shown in Figure-5.
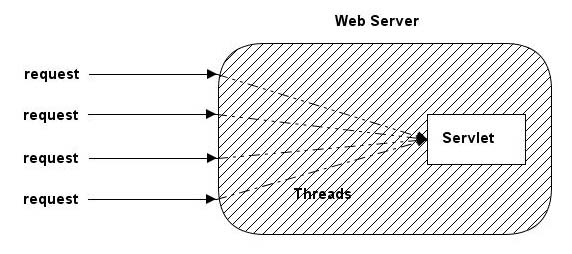
Figure-5 A way of handling Servlet requests
The init method of the servlet is called when the servlet is first created and each time the server receives a request for a servlet, the server spawns a new thread calls service method.
The service method checks the HTTP request type (GET, SET, PUT, DELETE, etc.) and calls doGet, doPost, doPut, doDelete, etc. method as appropriate.
Finally, the server may decide to remove a previous loaded servlets. In this case, the server calls destroy method of the servlet.
Servlet Scope Objects
There are four scope objects in servlets which enables sharing information between web components. The scope objects and their corresponding Java classes are listed below:
• Web Context – javax.servlet.ServletContext
• Session – javax.servlet.http.HttpSession
• Request – javax.servlet.HttpServletRequest
• Page – javax.servlet.jsp.PageContext
You can get attribute values from servlet scope objects using getAttribute method and set new values of attributes using setAttribute method. For example, you can get the client’s IP address by calling getRemoteAddr method of HttpServletRequest class.
Let’s develop an example on how to use servlet scope objects. In this example, we will print the information about the server which hosts our servlet.
|
The source code shown in this section can be found in ServerInfoServlet project. |
In our example, we will use the following methods to get the information about the server which hosts the client:
public String getServerName()
public String getServerPort()
public String getServletContext().getServerInfo()
Figure-6 shows processRequestMethod of ServerInfoServlet servlet and Figure-7 shows the output of the servlet in a browser.
| ..........
public class ServerInfoServlet extends HttpServlet { .......... * @param request servlet request * @param request servlet response */ .......... protected void processRequest (HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException { ..........response.setContentType(“text/html;charset=UTF-8”); ..........PrintWriter out = response.getWriter(); .......... ..........Out.println(“< html >”); ..........Out.println(“< head >”); ..........Out.println(“< title >Servlet ServerInfoServlet< /title >”); ..........Out.println(“< /head >”); .......... ..........Out.println(“< body >”); ..........Out.println(“< p >Server Name:+request.getServerName()+”< br >”); ..........Out.println(“ Server Port :+request.getServerPort()+”< br >”); ..........Out.println(“Server Path:+request.getServerPath()+”< /p >”); .......... ..........Out.println(“< /html >”); .......... } |
Figure-6 ProcessRequest method used in ServerInfoServlet servlet
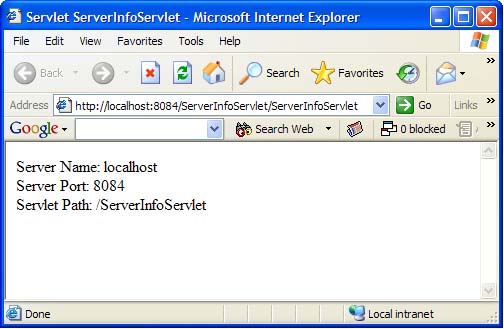
Figure-7 ServerInfoServlet servlet running in a browser
Error Handling
There are two ways to handle errors in servlets. You can send an error message or throw a ServletException.
For example, if a servlet can not find the requested file, it can display a 404 (“File Not Found”) message to the user by using the following command instead of directly writing the output to the PrintWriter object:
response.sendError(HttpServletResponse.SC_NOT_FOUND)
There are several other HTTP error codes which can be sent to the client. Some of the important ones are listed in Table-1. You can search on the internet about the details of those messages if they are not clear for you.
|
Mnemonic |
Code |
Message |
|
SC_OK |
200 |
OK |
|
SC_NO_CONTENT |
204 |
No Content |
|
SC_MOVED_PERMANENTLY |
301 |
Moved Permanently |
|
SC_MOVED_ TEMPORARILY |
[catlist id=173].
