VB.NET 2005 Tutorials : Testing a Windows Application
In this tutorial you will learn how to Test a Windows Application, Creating Unit Tests, Generating an ASP.NET Unit Test, benefits of unit testing, Integration Testing, Different approaches to Integration Testing, Regression Testing, goals of regression testing and Testing International Applications.
Testing
An application is software is created to function efficiently given the necessary parameters. Developers are conscious that, even in the most efficiently created software, errors of a certain nature can occur and must be provided for at design time. Yet other errors could occur at runtime and therefore applications need to be tested and debugged at runtime too. Therefore testing and debugging applications are an important part of application development. Visual Studio.NET provides the developer with several tools that he can use for testing and debugging the applications within the Integrated development environment (IDE).
Testing is the process of executing a program with the intention of finding errors. The application will be tested for usability, reliability and robustness also. The process may be manual, automated or a mixture of the two techniques.
The number of ways in which the application can be tested and debugged in Visual studio.NET demands that the user create a test plan beforehand. The developer can add a test project. He can test for performance, international settings or an existing test can be opened. To this end he must chalk out:
1. What kind of tests are to be created?
2. What is the type of load test that will be required?
3. Will the developer be required to execute a manual test?
4. How will the tests be managed?
5. What will be measured in the test–functionality, validation, performance or others?
Incremental testing is a modern approach to testing that proves useful while attempting rapid application development. This process is intended to be used while the application is being built. The levels of testing involved are : Unit testing, Integration testing and regression testing.
Unit tests are used when elementary units of an application are to be tested. Integration testing tests the integration of two or more units and the subsystems of those units. Regression testing is resorted to when bugs discovered in the first two types of testing are fixed and the unit and the integration of units have to be tested again for compatibility.
Creating Unit Tests
Let us presume that we have a project that has both public methods and private methods. The project has to be opened and we have to create unit tests for public and private methods. The next task is to run the tests on the projects code; find and correct the errors.
ASP .NET test projects can be created in any of the two ways mentioned below:
(1) By generating the ASP.NET unit test.
(2) By configuring an existing unit test as an ASP.NET unit test.
Generating an ASP.NET Unit Test
1. Create an ASP.NET application within the Visual Studio solution.
2. Add a class to the project,
3. Finally, generate a unit test from that class.
4. We will use the existing application to provide support for this.
5. Add a class to this project. To do this, in Solution Explorer, right-click the Windows Application and then click Add and then click class.
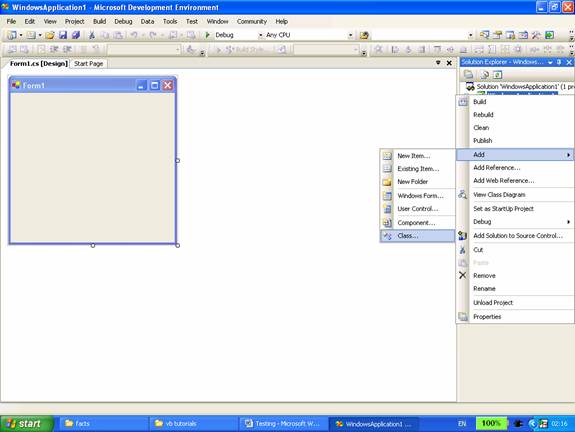
6. In the dialog box click Class, and then click Add.
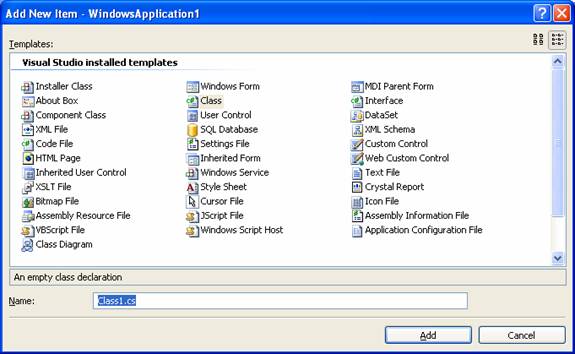
7. Note that a new class has been added.
Now we will generate an ASP.NET unit test.
(1) To do this, first open the new class file by double-clicking it in Solution Explorer.
(2) Right-click within the class in the class file. In the context menu and click on “Create Tests.”
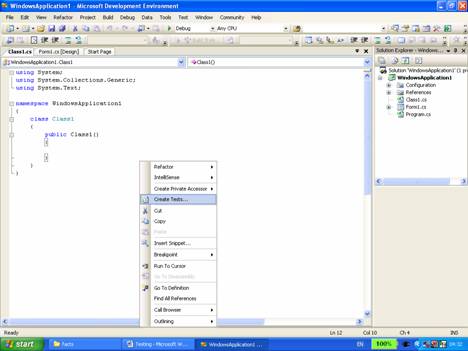
{mospagebreak}
.
.
(3) In the Unit Test Generation dialog box select the unit for which the test has to be generated and click Generate.
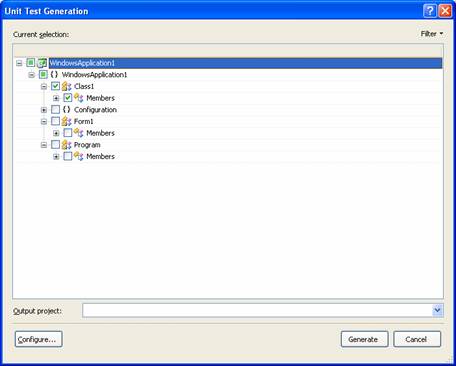
Once the output project has been specified a new ASP.NET unit test is added to a file in your test project.
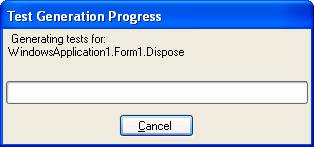
Note that a number of files have been created under the Test project including a localtestrun.testrunconfig file.
To see the unit test, open the localtestrun.testrunconfig file and scroll to the end. The attributes that are necessary to run a unit test as an ASP.NET unit test have been automatically set. The content of the test file is given below:
Click here to view sample code
The major benefits to be had from unit testing are
1. It allows the developer test parts of an application without waiting for the other parts to be available.
2. Exceptional conditions can be tested for the unit
3. The debugging process is simplified by limiting the search for bugs to a small unit rather than the complete application.
4. It helps avoid lengthy compile-build-debug cycles when debugging difficult problems.
5. Detection and removal of defects can be done at a much lower cost.
Integration Testing
The purpose of this kind of testing is to verify whether the major subsystems of the application are integrated. It helps in uncovering the errors that may arise due to conflicts between different units of an application. Integration testing is performed in different ways.
Bottom Up Approach: The testing is commenced from the smallest subsystem and progresses up the hierarchy to cover the whole system. This methodology requires the developer to write a number of test driver programs that test the integration between the subsystems.
Top down Approach: This begins at the top. The top level interfaces are first tested and then the smaller sub systems are examined. Stubs are written for modules that are not ready for testing.
Umbrella Approach: The focus in this methodology is on testing the modules that have a high degree of user interaction. Stubs are used in place of process intensive modules. This enables the developer test the graphical user interface and improves the functionality of the interface.
Regression Testing
Regression testing is performed whenever the program is modified. The process involves the rerun of all the tests mentioned in the preceding sections. It has two main goals:
- Verification of known bugs that were corrected
- Verification of new bugs.
Testing International Applications
Applications created for international usage are to be tested by checking for the language, the country and dependencies. The following factors are to be considered when testing such applications:
- Whether the application’s data and user interface conform to the locale’s standards for date, time, numeric values, currency, list separators and measurements.
- Whether the application runs on different languages and culture variants.
- If Unicode has not been used in the application the culture/locale code of the operating system will have to be set to the localized version of the application.
- The Input data in the language should be supported by the localized version.
In this section of the lesson we have focused upon the testing of Windows applications. In the sections that follow we shall briefly look at tracing windows applications.
[catlist id=175].
