Radix sort is a sorting algorithm that sorts the data, integers for example, by splitting the numbers into individual digits and comparing the individual digits sharing the same significant position.
Also, a positional notation is required, because instead of integers there could be strings of characters or floating point numbers.
The radix sort can be classified into 2 types: LSD (least significant digit) or MSD (most significant digit). The LSD sorting type begins from the least significant digit to the most significant digit and the MSD works the other way around.
Note: having the number 150, the number 0 is the least significant digit and 1 is the most significant digit.
Step by step example :
Having the following list, let’s try to use radix sort to arrange the numbers from lowest to greatest:
Unsorted list: 12, 8, 92, 7, 100, 500. Because there are numbers with 3 digits, we can write the initial list like this: 012, 008, 092, 007, 100, 500.
Now by using the LSD, the sorting may begin with step 1:
Write all the numbers that have one of the following digit as the LSD of the numbers from the list:
0:100, 500
1:-
2:012, 092
3:-
4:-
5:-
6:-
7:007
8:008
9:-
Also, if you have two numbers with the same digit like 012 and 092, you write them in the order from the list.
Now, the order of the numbers according to step 1 is: 100, 500, 012, 092, 007, 008, which differs a bit from the initial list.
We repeat step 1, but now we use the second digit :
0:100, 500, 007, 008
1:012
2:-
3:-
4:-
5:-
6:-
7:-
8:-
9:092
After step 2, the order is: 100, 500, 007, 008, 012, 092.
Step 3, using the MSB:
0:007, 008, 012, 092
1: 100
2:-
3:-
4:-
5: 500
6:-
7:-
8:-
9:-
The final list is the sorted one: 007, 008, 012, 092, 100, 500.
Sample code:
#include < iostream >using namespace std;
#define MAX 100void print(int *a, int n) //Prints the numbers of an array
{int i;
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
cout << " " << a[i];
}void radixsort(int *a, int n)
{int i, b[MAX], m = 0, exp = 1;
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
{if (a[i] > m)
m = a[i];
}while (m / exp > 0)
{int bucket[10] ={0};
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
bucket[a[i] / exp % 10]++;
for (i = 1; i < 10; i++)
bucket[i] += bucket[i - 1];
for (i = n - 1; i >= 0; i--)
b[--bucket[a[i] / exp % 10]] = a[i];
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
a[i] = b[i];
exp *= 10;
cout << "nPASS : ";
print(a, n); //Prints the results from the first pass
}}int main()
{int arr[MAX];
int i, n;
cout << "Enter total elements n < " << MAX << endl;
cin>>n;
cout << "Enter " << n << " Elements : " << endl;
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
cin>>arr[i];
cout<<"nARRAY : ";
print(&arr[0], n);
radixsort(&arr[0], n);
cout << "nSORTED : ";
print(&arr[0], n);
printf("n");
return 0;
}
Output:
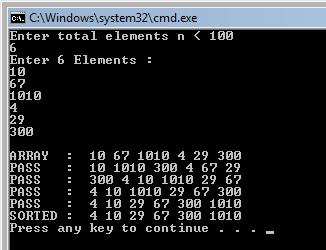
Code explanation:
int i, b[MAX], m = 0, exp = 1;
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
{if (a[i] > m)
m = a[i];
}while (m / exp > 0)
{int bucket[10] ={0};
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
bucket[a[i] / exp % 10]++;
for (i = 1; i < 10; i++)
bucket[i] += bucket[i - 1];
for (i = n - 1; i >= 0; i--)
b[--bucket[a[i] / exp % 10]] = a[i];
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
a[i] = b[i];
exp *= 10;
cout << "nPASS : ";
print(a, n); //Prints the results from the first pass
}
At the first for loop, the variable m will store the highest number from the array.
At the while loop, the condition is to check if the number still has digits, and while this is true, a bucket (an array) with maxim 10 storage places (the values from 0 to 9) will store the proper numbers, just like in the example from above. At the end of the while loop the exp must increase by a factor of 10 compared to the previous one, and at the next check of the while loop, the condition will be tested to see of the number of digits is greater than 0.
Complexity:
The time complexity of the algorithm is as follows: Suppose that the n input numbers have maximum k digits. Then the Counting Sort procedure is called a total of k times. Counting Sort is a linear, or O(n) algorithm. So the entire Radix Sort procedure takes O(k*n) time. If the numbers are of finite size, the algorithm runs in O(n) asymptotic time.
Advantages:
- if it’s implemented in Java, it would be faster than QuickSort or HeapSort;
- is stable, meaning it preserves existing order of equal keys.
- is quite good on small keys.
Disadvantages:
- does not work well when you have very long keys, because the total sorting time is proportional to key length and to the number of items to sort.
- you have to write an unconventional compare routine.
- It requires fixed size keys, and some standard way of breaking the keys into pieces.
Conclusion:
Radix Sort is a clever and intuitive little sorting algorithm. Radix Sort can also take up more space than other sorting algorithms, since in addition to the array that will be sorted, you need to have a sub-list for each of the possible digits or letters. If you are sorting pure English words, you will need at least 26 different sub-lists, and if you are sorting alphanumeric words or sentences, you will probably need more than 40 sub-lists in all. Also, it depends on the digits or letters, so for every different type of data, the programmer has to rewrite the sorting algorithm, which is quite a big drawback.
[catlist id=197].
