Let us say that the order relation that was defined the in introduction lesson was a partial one, for example:
a1 < a0, a1 < a2 < a3.
The problem is to determine a list of order, in which if ai < aj then ai will come before aj in the final sorted list .
For example, our list could be :
a1, a0, a2, a3
or
a1, a2, a0, a3
or
a1, a2, a3, a0
Any partial ordered list can be sorted topological.
For a graph, a topological sort of a directed graph refers to an ordering of the vertices, that for every edge u,v, u comes before v in the ordering.
A topological sort is possible only if the graph has no directed cycles, which it means it must be a directed acyclic graph or DAG. A cycle in a graph means having 3 nodes A, B and C, there is a path from A to B, from B to C and from C to A, which creates a cycle.
Step by step example:
Having the following DAG:
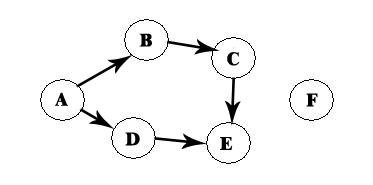
An order could be A -> B D -> E C-> D F, but this is wrong, it is not an topological order!
First, choose from the vertices the one that has no predecessors :
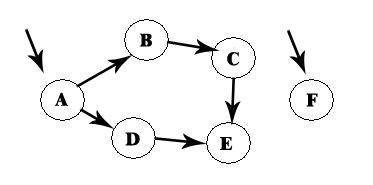
Let us choose A, so we delete A and all the lines from there, and A will be the first element:
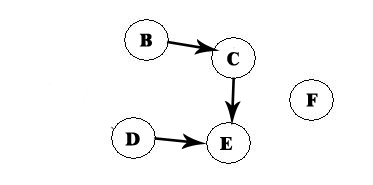
Then again we choose the element that has no predecessors:
Choose D, and to the same like in the previous case and we now have A -> D:
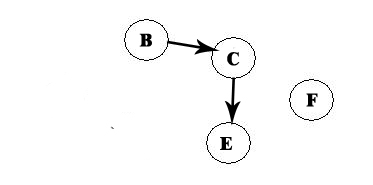
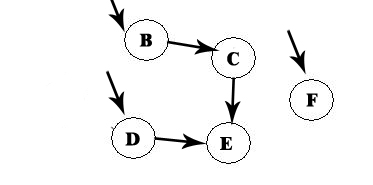
We repeat the process:
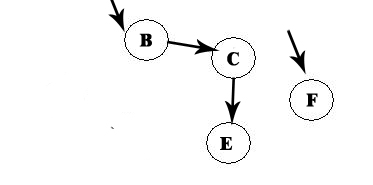
We remove F, and now we have A -> D -> F:
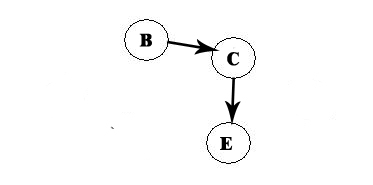
B is the only option left:
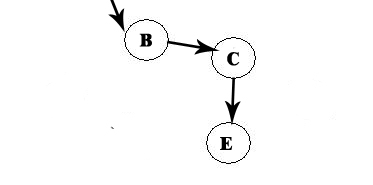
A -> D -> F -> B
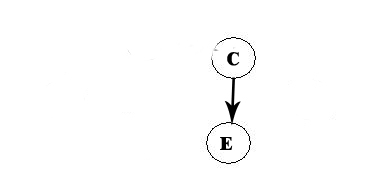
We now choose C:
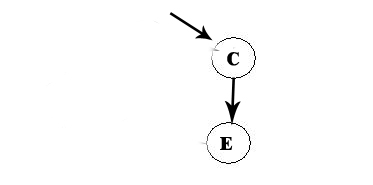
A -> D -> F -> B -> C
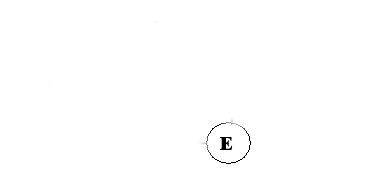
And all the remains is E. The list will be A -> D -> F -> B -> C -> E.
Sample code:
#include < iostream>using namespace std;
# include < math.h >int main()
{int i,j,k,n,a[10][10],indeg[10],flag[10],count=0;
cout << "Enter the no of vertices:";
cin >> n;
cout << "Enter the incidence matrix:" ;
for(i=0;i< n;i++)
for(j=0;j< n;j++)
cin>>a[i][j];
for(i=0;i< n;i++)
{indeg[i]=0;
flag[i]=0;
}for(i=0;i< n;i++)
for(j=0;j< n;j++)
indeg[i]=indeg[i]+a[j][i];
cout << "The topological order is:" ;
while(count< n)
{for(k=0;k< n;k++)
{if((indeg[k]==0) && (flag[k]==0))
{cout << (k+1) ;
flag [k]=1;
}for(i=0;i< n;i++)
{if(a[i][k]==1)
indeg[k]--;
}}count++;
}return 0;
}
Output:
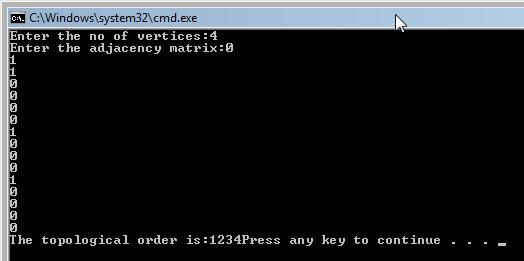
Code explanation:
At first, all the vertices are counted, I refer to the number of predecessors for each vertex. Then, a vertex with 0 is found (0 because it must not have any predecessors for the topological sort to work). It is removed, then the degrees are updated. In this sample code, the vertices are inserted in the form of an incidence matrix (you can read about this in the lesson regarding graph theory). As for this example, the matrix is :
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | |
| 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 4 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
A visual representation of the graph:
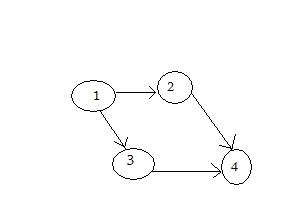
The data will be inserted line by line, from the above matrix for the first vertex 1 is 0, 1, 1, 0, then for the vertex 2 is 0, 0, 0, 1 and so on.
Complexity:
How many operations are needed to compute the in-degrees? Depends on the representation:
Adjacency lists: O(|E|)
Matrix: O(|V|2)
Note that if the graph is complete |E| = O(|V|2).
Conclusion:
Topological sort is used for partial defined orders. In recent years, the algorithm was developed for parallel computation. In general use, this algorithm is used in cases for which a graphic model is available for people to understand bigger problems.
[catlist id=197].
